Oncology
Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease
Targeting Both Inflammation and Fibrosis in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease
Overview
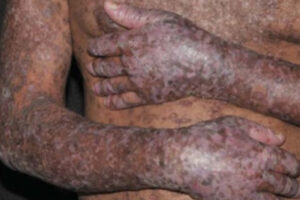
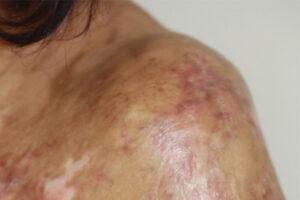
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) involves both inflammatory and fibrotic pathologies. While most treatments for cGVHD target the inflammation, new and emerging treatments are designed to more directly target the fibrosis as well.
Expert Commentary
Corey Cutler,, MD, MPH, FRCPC
|
|
“The final pathway in cGVHD often involves prosclerotic mechanisms, with monocytes, macrophages, and other cells that lay down collagen. . . . ”
The pathogenesis of cGVHD is associated with both inflammatory and fibrotic mechanisms. The final pathway in cGVHD often involves prosclerotic mechanisms, with monocytes, macrophages, and other cells that lay down collagen (eg, myofibroblasts and fibroblasts). The end result in most cases is scarring or fibrosis. Fibrosis is not static; for example, there is always cell turnover within a scar, although it can take a very long time for a scar to revert.
Most treatments for cGVHD are immunosuppressive and do not specifically target fibrosis; however, belumosudil and axatilimab, the latter of which is not yet approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, specifically target the fibrotic phases of cGVHD. Belumosudil targets both inflammation and fibrosis because it hits several pathways that are involved in the pathobiology of cGVHD, both upstream (at the level of the germinal center and in preventing the elaboration of inflammatory Th17 cells) and then, much later, downstream with collagen-laying cells. Specifically, belumosudil targets fibrosis via ROCK2, which is important for myofibroblast differentiation, and it can also block TGFB-mediated fibrosis. In addition, belumosudil changes STAT3 and STAT5 signaling at the level of the germinal center, which rebalances the immunology of cGVHD. In theory, axatilimab only targets the sclerotic part of cGVHD by specifically targeting the monocyte macrophage lineage, but we are also learning that it actually might be active in the inflammatory pathways that are involved in cGVHD.
The ultimate role of these agents in the management of cGVHD remains to be determined, as we do not fully understand all of the biologic processes that are involved. The use of a ROCK2 inhibitor such as belumosudil seems particularly appealing for evaluation as a potential frontline agent because it has a low toxicity profile and will likely be the best tolerated with chronic use, although this needs to be shown in clinical trials. The understanding of the biologic processes that are involved in cGVHD continues to develop and unfold. All of these novel therapies should be evaluated in clinical trials that investigate their use earlier in the disease course. Additionally, combinations that target different pathways should be explored.
References
Braun LM, Zeiser R. Kinase inhibition as treatment for acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 17;12:760199. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.760199
Cutler C, Lee SJ, Arai S, et al. Belumosudil for chronic graft-versus-host disease after 2 or more prior lines of therapy: the ROCKstar study [published correction appears in Blood. 2022;139(11):1772]. Blood. 2021;138(22):2278-2289. doi:10.1182/blood.2021012021
Cutler C. Treating inflammation and fibrosis in chronic GVHD: two birds, one ROCK. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(17):1942-1945. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.00214
Flynn R, Du J, Veenstra RG, et al. Increased T follicular helper cells and germinal center B cells are required for cGVHD and bronchiolitis obliterans. Blood. 2014;123(25):3988-3998. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-03-562231
Jagasia M, Lazaryan A, Bachier CR, et al. ROCK2 inhibition with belumosudil (KD025) for the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(17):1888-1898. doi:10.1200/jco.20.02754
Lee SJ, Arora M, Defilipp Z, et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of axatilimab, a CSF-1R humanized antibody, for chronic graft-versus-host disease after 2 or more lines of systemic treatment. Blood. 2021;138(suppl 1):263. doi:10.1182/blood-2021-146050
Rozmus J. Monogenic immune diseases provide insights into the mechanisms and treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Front Immunol. 2020;11:574569. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.574569
Zanin-Zhorov A, Blazar BR. ROCK2, a critical regulator of immune modulation and fibrosis has emerged as a therapeutic target in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Clin Immunol. 2021;230:108823. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2021.108823