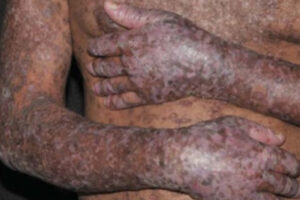
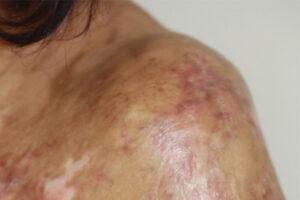
Oncology
Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease
Targeting the Biology of Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease
Overview
The manifestations and severity of chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) are highly variable and are influenced by cytokines and downstream pathways that mediate inflammation and fibrosis. Research on targeting these pathways is burgeoning and has led to US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals.
Expert Commentary
Corey Cutler,, MD, MPH, FRCPC
|
|
“There are a few convergent pathways that we can try to target for the management of fibrosis in cGVHD, and recent FDA approvals reflect the work being done in this area.”
When we think about the pathobiology of cGVHD, we start with inflammation and dysregulated immunity, but, ultimately, we end up with sclerosis and fibrosis. There are a few convergent pathways that we can try to target for the management of fibrosis in cGVHD, and recent FDA approvals reflect the work being done in this area.
Belumosudil and ruxolitinib are among the most recently FDA-approved treatments for cGVHD, with approvals granted in 2021, whereas ibrutinib received approval for cGVHD back in 2017. All 3 of these agents are indicated for use after the failure of prior lines of therapy in adults and in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with cGVHD. Ibrutinib is not an antifibrotic agent per se, as it works at the level of the B-cell receptor by blocking Bruton tyrosine kinase, which is likely a more proximal step in cGVHD (ie, at the level of the germinal center and the inflammatory cascades that lead to cGVHD). Similarly, ruxolitinib inhibits the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway, which mediates signals for interleukin 6 and interferon gamma, predominantly inflammatory-type pathways.
Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinases (ROCKs) are key coordinators of tissue response to injury, regulating multiple functions, and they exist in different isoforms. The ROCK2 isoform drives a proinflammatory Th17 cell response; therefore, ROCK2 inhibition has anti-inflammatory activity at the level of the germinal center. Furthermore, the selective inhibition of ROCK2 by belumosudil reduces fibrosis by downregulating both transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β1) signaling and profibrotic gene expression.
I think that the medical community is optimistic about belumosudil for a couple of reasons. First, the high overall response rates, ranging from 62% to 87%, were reported in all subgroups analyzed. And this was a cohort of patients who had already received 2 to 5 lines of therapy, including ibrutinib and ruxolitinib in many instances. In addition, mechanistically, ROCK2 inhibition has the potential to reverse fibrosis, and so there is interest in exploring the efficacy of this agent in subtypes of GVHD with fibrosis as one of the prominent features.
If we think about the pathways that are known to be important in fibrosis, we know that TGF-β1 is an important cytokine, so agents such as nintedanib that inhibit TGF-β signaling might have applications early in cGVHD. There are now inhibitors against the colony stimulating factor 1 receptor found on monocytes and macrophages, and it might be possible to prevent fibrosis by preventing the inflammatory cells from getting into the tissues (ie, using chemokine inhibitors to prevent the migration of these cells into the target organs). Finally, something that is very interesting is blocking the production of collagen intracellularly by using agents that attack the collagen chaperone HSP47. Those have been tested topically in ocular GVHD; at some point, they will hopefully be tested more broadly in systemic GVHD, as well.
References
Arora M, Jagasia M, Di Stasi A, et al. Phase 1 study of axatilimab (SNDX-6352), a CSF-1R humanized antibody, for chronic graft-versus-host disease after 2 or more lines of systemic treatment [abstract 358]. Abstract presented at: 62nd American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting and Exposition; December 5-8, 2020.
ClinicalTrials.gov. Nintedanib in patients with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (NINBOST2018). Updated July 8, 2021. Accessed October 7, 2021. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03805477
Cutler CS, Lee SJ, Arai S, et al. Belumosudil for chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) after 2 or more prior lines of therapy: the ROCKstar study. Blood. 2021 Jul 15;blood.2021012021. doi:10.1182/blood.2021012021
Holtzman NG, Im A, Ostojic A, et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib in refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD): preliminary analysis results of a phase 1/2 study [abstract 357]. Abstract presented at: 62nd American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting and Exposition; December 5-8, 2020.
MacDonald KP, Blazar BR, Hill GR. Cytokine mediators of chronic graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2452-2463. doi:10.1172/JCI90593
Miklos D, Cutler CS, Arora M, et al. Ibrutinib for chronic graft-versus-host disease after failure of prior therapy. Blood. 2017;130(21):2243-2250. doi:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-07-793786
Rangarajan S, Kurundkar A, Kurundkar D, et al. Novel mechanisms for the antifibrotic action of nintedanib. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016;54(1):51-59. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2014-0445OC
Saidu NEB, Bonini C, Dickinson A, et al. New approaches for the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease: current status and future directions. Front Immunol. 2020;11:578314. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.578314
Zanin-Zhorov A, Blazar BR. ROCK2, a critical regulator of immune modulation and fibrosis has emerged as a therapeutic target in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Clin Immunol. 2021;230:108823. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2021.108823
Zeiser R, Burchert A, Lengerke C, et al. Ruxolitinib in corticosteroid-refractory graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a multicenter survey. Leukemia. 2015;29(10):2062-2068. doi:10.1038/leu.2015.212
Zeiser R, Polverelli N, Ram R, et al. Ruxolitinib (RUX) vs best available therapy (BAT) in patients (Pts) with glucocorticoid-refractory chronic graft-vs-host disease (cGVHD): primary findings from the phase 3, randomized REACH3 study [abstract 82]. Abstract presented at: 2021 Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings of ASTCT and CIBMTR; February 8-12, 2021.